A media-based aquaponics system, also called flood and drain, is the most common small-scale aquaponics system popular with do-it-yourself (DIY) backyard home systems. Media-based systems designs are simple and efficient with space and have a low initial cost suitable for beginners in aquaponics.
How Media Based Aquaponics Systems Work
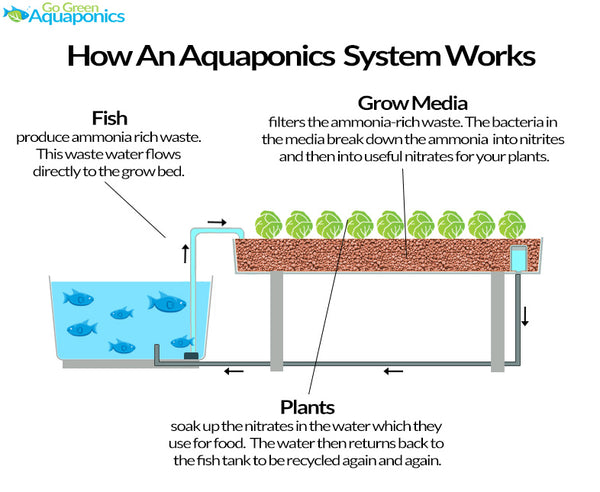
The media-based consists of a grow bed filled with grow media (expanded clay pebbles, gravel, lava rock) into which the vegetables are planted. The water from the fish tank is pumped or flows by gravity into the grow beds so that the plants can access the nutrients. The grow media are porous to allow them to hold the water longer for more efficient nutrient uptake and filter out the water to prevent solids materials and other organisms from entering the fish tank.
The grow bed serves as both the mechanical and biological filter and location for mineralization. The grow beds also host the colony of nitrifying bacteria and provide a place for the plants to grow.
On exiting the grow beds, the water flows to the sump tank by gravity. At this point, the water is clean and free of solids and then pumped back into the fish tank. The water entering the fish tank causes the water level to rise and overflow from the fish tank back into the grow beds, completing the cycle.
Some media-based aquaponics systems are run by flooding and draining the grow beds, using a bell siphon to drain the water when it reaches a saturation point. Once the water reaches a certain level on the grow bed, the bell siphon will drain the water from the grow bed. This process will draw oxygen back down into the grow bed to benefit the microbes and the plants. This is a continuous regular cycle that provides all the necessary nutrients for the plants to grow without fertilizers.
Other grow-bed irrigation methods use a constant water flow, either entering one side of the bed and exiting the other or distributed through a drip irrigation array.
 Filtration
Filtration
The grow media can serve as very efficient filters for mechanical and biological filtration in a media-based aquaponics system. The media-based system utilizes the combination of filters for the water and plant growing area for the plants. In addition, it also provides a place for mineralization to occur. However, high stocking densities can overwhelm the mechanical filtration that can risk having the media clogged and producing dangerous anaerobic spots.
- Mechanical Filter
The grow media functions as a large filter, capturing and containing the solid fish wastes, and other floating debris. The captured solid wastes will break down over time and be mineralized. A properly balanced media-based aquaponics system will process all the solid wastes. When the grow bed and grow media are not appropriately sized for the stocking density, the grow bed can be clogged with solids. To avoid clogging, be sure that the stocking density, feeding ratio, and feed rate are in the right ratio.
- Biological Filtration
Of all aquaponics methods, the media-based system has the most biological filtration because of the growing media's presence on which the bacteria can grow. However, the biofiltration capacity will be lost or limited if the grow bed and grow media become anoxic if the temperatures drop or if the water quality is low.
The Three Zones Of Media-Based Aquaponics System
There are three grow bed zones in the media-based aquaponics system, and each zone has different functions in the system.
Zone 1 - The Surface or Dry Zone. This area is within the first 1- 2" (5cm) of the grow bed. This area is called the dry zone and functions as a light barrier, preventing the light from hitting the water directly, which can lead to algae growth. This zone prevents the growth of fungus and other harmful bacteria at the base of the plant stem. The beneficial bacteria are sensitive to direct sunlight, and this zone also helps minimize evaporation from the beds by covering the wet zone from the direct light.
Zone 2 - The root zone. This is where the plants' roots grow and where all pants activity takes place. Zone 2 is around the 4 - 6" (10-15cm) area of the grow bed and is the area that is regularly flooded and drained.
For the flood and drain cycle, the incoming water helps spread moisture, nutrients, and incoming solid fish waste particles into the area. When it's time for the flood and drain cycle, the drain parts allow the water to drain away completely. This draining allows for the efficient delivery of the oxygen-rich air into the plants' root area.
If not using a flood and drain technique, this zone is where the water flows through the medium. In this zone, the worms are responsible for breaking down and minimizing solid waste, which releases nutrients throughout the system.
Zone 3- The solid collection and mineralization zone. This is the last zone which is in the last 2" (5cm) of the grow bed that remains permanently wet. In this zone, the small solid wastes accumulate, so the organisms that are the most active in mineralization are located here. These organisms break down the waste into smaller fractions and molecules that can be absorbed by the plants through the process of mineralization.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Media-Based System
Advantages
- Relatively simple and inexpensive.
- Suitable for all kinds of plants, from leafy greens to larger fruiting plants.
- Minimal cleaning is required.
- For a further breakdown of fish waste, red worms can be added to the gravel bed.
- The media perform a filtering action, preventing debris from returning to the tank.
- The air is present between media particles, supplying oxygen to the roots.
- Suitable for hobby applications, home gardens, and as part of the commercial farm.
Disadvantages
- A good-quality medium can be relatively expensive.
- The pore spaces in the medium may get clogged over time, causing anaerobic conditions that are poor for your plants.
- It can require cleaning of the grow bed.
- By itself, this style system is not usually suitable for commercial purposes due to lower productivity and difficulty in a large-scale implementation.
- The media beds are heavy and need a strong, rigid structure.
Components of a Media Based Aquaponics System
It is important to have materials comfortable for the farmer. The ultimate aquaponics beginner’s guide discusses all the necessary materials needed in setting up an aquaponics system. These are the essential criteria for the materials that will be used in the media-based system.
- Grow media must have a large surface area for bacterial growth.
- Materials must be neutral pH and inert (non-toxic).
- Must have good drainage properties.
- Easy to work with.
- Sufficient space for air and water to flow within the medium.
- Durable and cost-effective.
- Lightweight
1. Fish Tank
Fish tanks are a critical component of aquaponics. Fish require specific conditions to thrive and survive. Therefore, the fish tank should be chosen wisely. There are important aspects that need to be considered in choosing your fish tank.
Shape
Although any tank's shape will work, round tanks with flat bottoms are recommended for aquaponics. A round shape tank allows water to circulate uniformly and transports solid wastes towards the tank's center. Square tank with flat bottom works, but it requires active solid waste removal. Tank shapes affect water circulation, and it's risky to have a tank with poor circulation. Artistically shaped tanks with many curves and bends can create dead sp[ots in the water with no circulation. These areas gather wastes and create dangerous anoxic conditions for the fish. It is important to choose a tank that fits the characteristics of the aquatic species reared because many species of bottom-dwelling fish show better growth and less stress with adequate horizontal space.
Material
The material should be either a strong, inert plastic or fiberglass because of their durability and long life span. Plastic and fiberglass are easy to install for plumbing and are fairly light. Metal is not advisable because of rust. If you're using a plastic container, make sure that they are food-grade and UV-resistant because direct sunlight can destroy the plastic.
Color
White or other light-colored fish tanks are advisable because they allow easy viewing of the fish inside the tanks. White tanks also reflect the sunlight and keep the water cool.
2. Grow Bed
One of the most important components in the media bed system is the grow bed. The grow bed is where you grow your plants. Make sure your grow bed is:
- made of food-grade materials that will not leak unwanted chemicals into the water or affect the water pH.
- Strong enough to hold the water and growing media.
- Able to withstand different weather conditions.
- It can be connected to other components easily through simple plumbing parts.
- It can be placed near the other components.
Shape
The standard shape for a media bed is a rectangle. Large grow beds can be used, but they require support to hold their weight. However, the grow beds should not be so wide that the farmer/ operator cannot reach across, at least half-way.
Depth and Size
A media-based grow bed needs to have the right depth and size related to the fish volume and provide adequate filtration for the nutrient-rich water. The grow bed depth is important because it determines what types of vegetables can be grown.
Grow beds should be about 12 inches in depth to optimize plant growth and for the cultivation of beneficial ecosystems in the bed. When selecting your grow bed, the rule of thumb is to use a 1:1 ratio of your grow bed to the fish tank in small systems. This means that the grow bed volume should be equal to the fish tank volume. This is not a hard rule but a good rule to follow when starting out.
3. Grow Media
Many materials can be used as a medium in a media-based system. However, the media must be organic and have an adequate surface area to allow bacteria to grow and water to flow to the plants' roots. The medium must have a neutral pH so that the water quality will not be affected. It is good to wash the media thoroughly before placing it into your grow bed to ensure that there are no dangerous particles that can potentially harm the fish.
Grow Media Options
Gravel
It is the least expensive and most readily available grow medium, ¾" gravel is best for supporting taller plants, and it doesn't get clogged like smaller pea gravel. Gravel thought is heavy and is not as preferred for growing smaller plants because it can be rough on the hands. Another drawback of using gravel is that it does not hold water efficiently, so it can sometimes be more difficult to colonize the needed bacteria in your system. It is important to perform a vinegar test of gravel before placing it in your system, as limestone is sometimes present in the gravel.
Clay pebbles
LECA (Lightweight Expanded Clay Aggregate) are balls of clay processed at a very high temperature to form a highly effective growing medium. Clay pebbles are lightweight enough to move around when planting easily and heavy enough to provide adequate support for small to medium plants. (you may need to support/tie-up tall plants like corn, for example) They are also non-degradable, non-toxic, and pH neutral. Clay pebbles are more expensive compared to the other mediums, but because it is reusable, lightweight, and pH neutral; clay pebbles are an investment that will last for many years.
Lava Rock
The naturally created lava rock cools rapidly, which gives no time for the air to escape, effectively trapping it. This trapped air creates a highly porous surface, increasing the area of the rock and creating plenty of openings for the nitrifying bacteria to live. Lava rock is light and has a neutral pH, so it won't affect the balance of your system. Lava rock can be sharp, though, so you will want to use it with caution.
4. Bell Siphon
A Bell Siphon, also known as an Auto Siphon, is a mechanical device used to regulate the water flow quickly and efficiently in an aquaponic system. The siphon automatically allows water from the grow bed to be drained into the fish tank. Then the water is pumped from the fish tank into the grow bed. The siphon also maintains a minimum water level and drains any excess water.
Best Plants To Grow In Media Based Aquaponics System
Vegetables have different nutrient demand. In aquaponics, plants are categorized based on their nutrient demand.
- Low-nutrient-demand plants include leafy greens and herbs like chard, lettuce, basil, mint, chives, parsley, coriander, pak choy, watercress, and legumes such as peas and beans.
- Medium-nutrient demand plants are cabbage, kale, cauliflower, broccoli, onions, carrots, and taro.
- High-nutrient-demand plants, also called nutrient hungry plants, are tomatoes, eggplants, cucumbers, strawberries, and peppers.
Your choice of plants will depend on the style of your grow bed. Our article What Are The Best Plants For Aquaponics discusses what plants grow best in an aquaponics system. In media-based aquaponics, it is possible to grow leafy greens, herbs, and fruiting vegetables at the same time, as long as the grow beds are the right depth. A media-based can also take advantage of mixed planting with better space management because shade-tolerant species can grow underneath taller plants. Large bulb and root crops, such as ginger, carrots, and turnips, are best grown in a media-based aquaponics system because the grow bed and grow media provide an excellent growing environment and adequate support to plants.
Other Types of Aquaponics Systems
The two other main types of aquaponic systems are Raft Systems, Nutrient Film Technique, or NFT.
Raft SystemThe raft system also is known as Deep Water Culture or Floating System. Plants are grown on rafts (polystyrene or foam boards) that float on top of the water in the raft tank. The nutrient-filled water flows continuously from the fish tank through the filtration process, then to the raft tank where the plants are grown, and then back to the fish tank. Most often, the raft tank is separate from the fish tank. Plants grow very fast in a raft system and can be an easy aquaponics system for the beginner aquaponics gardener to set up and maintain.
Since the development of aquaponics raft systems (DWC) on a commercial scale by Dr. Rakocy at the University of the Virgin Islands, many commercial aquaponics farms utilize this system because it allows the plants to grow faster and yield more crops. The Raft system is best suited for mass production of certain types of vegetables and leafy greens.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) System
The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) is an aquaponics method in which the plants are grown in a long narrow channel. NFT is both common in hydroponics and aquaponics due to its simple yet effective design. In NFT, a thin film of water flows continuously down each channel, providing the plant roots with water, nutrients, and oxygen. When the water reaches the end of the channel, it is pumped back to the fish tank. NFT uses both water and pumps to deliver nutrients to the plants, and the system requires a separate filter to clear the water of solids and biological waste before it's returned to the fish tank. This system is very efficient in its water use and is primarily used to cultivate greens with small roots systems. NFT is commonly used in the commercial aquaponic system but can also be used in a hobby system as long as it is filtered before it is used in NFT channels.
Conclusion
Your choice of aquaponics system depends on you and what you want. We hope this article helps you make more informed about the media-based aquaponics system and decide which system is right for you. If you want to learn more, subscribe to our mailing list to be notified of our next article; What is the Nutrient Film Technique Aquaponics System?



No comments:
Post a Comment